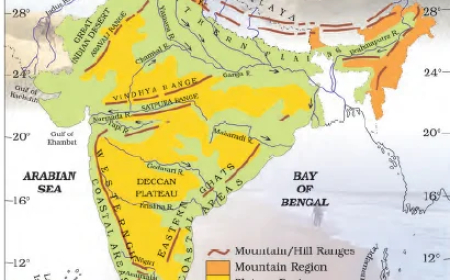
The Peninsular Plateaus- Deccan Plateau- Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats
Deccan Plateau- Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats comparison
Deccan Plateau
-
This physiographic division is the largest part of the plateau region of India.
-
The shape of this plateau is roughly triangular.
-
One of the sides of this triangle is marked by the line joining Kanyakumari with Rajmahal Hills, passing through the Eastern Ghats.
-
The second arm is marked by the Satpura Range, Mahadeo Hills, Maikal Range, and the Rajmahal Hills.
-
The third arm is marked by the Western Ghats.
-
The area of this plateau is about 7 lakh square kilometers, with
-
heights ranging from 500 to 1000 meters above sea level.
| Feature | Western Ghats | Eastern Ghats |
| Location | Runs parallel to the western coast of India | Runs parallel to the eastern coast of India This range is also called as Poorvadri. |
| Extent | From Gujarat to Tamil Nadu (north to south) | From Odisha to Tamil Nadu (north to south) |
| Length | About 1,600 km | About 1,750 km |
| Width | 50-80 km | 100-200 km |
| Average Elevation | 900-1600 meters | 600 meters |
| Highest Peak | Anamudi (2,695 meters) | Arma Konda (1,680 meters) |
| Geological Formation | Precambrian era rocks | Older than the Western Ghats, mostly metamorphic rocks |
| The northern part of this range is called as Sahyadris.The height of the Sahyadris increases from north to south. | ||
| Anaimudi is a sort of tri-junction of the Anaimalai Range, the Cardamom Hills and the Palani Hills. Kodaikanal is a beautiful hill resort situated on the Palani Hills |
Eastern Ghats join the Western Ghats at the Nilgiri hills, bordering Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. |
|
| Topography | Continuous range with high peaks | Discontinuous and broken by rivers |
| Climate | Tropical and subtropical, high rainfall | Mostly tropical, lower rainfall than Western Ghats |
| Rivers Originating | Godavari, Krishna, Kaveri, and many others | Rivers such as Vamsadhara, Nagavali, and others |
| Biodiversity | Rich in biodiversity, includes numerous endemic species | Less biodiversity compared to Western Ghats |
| Vegetation | Evergreen forests, deciduous forests, and montane forests | Mostly deciduous forests |
| Fauna | Tigers, elephants, gaur, and various endemic species | Less diverse fauna compared to Western Ghats |
| Significance | UNESCO World Heritage Site, biodiversity hotspot | Less recognized globally but important for local biodiversity |
| Human Settlements | Sparsely populated, numerous tribal communities | More populated, includes several urban centers |
| Agriculture | Plantation agriculture (tea, coffee, spices) | Mixed farming, less plantation agriculture |
| Protected Areas | Numerous national parks and wildlife sanctuaries (e.g., Silent Valley, Periyar) | Fewer national parks and wildlife sanctuaries (e.g., Similipal) |
| Economic Activities | Tourism, agriculture, hydroelectric projects | Agriculture, mining |
| Cultural Significance | Numerous ancient temples and cultural sites | Numerous ancient temples and cultural sites |
What's Your Reaction?