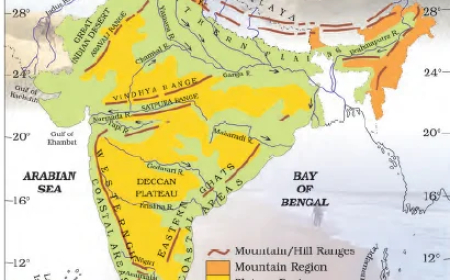
The Peninsular Plateaus-Central highlands
The Peninsular Plateaus-Central highlands
The Peninsular Plateaus-Central highlands
- The plateau region lies to the south of the Great Northern Plains.
- This is the largest physiographic division of our country.
- It covers an area of about 16 lakh sq.km (about half of the total area of the country).
- It is an old rocky plateau region.
- The topography consists of a series of plateaus and hill ranges interspersed with river valleys.
- Aravalli hills mark the north-western boundary of the plateau region.
- Its northern and north-eastern boundaries are marked by the Bundelkhand upland, Kaimur, and Rajmahal hills.
- The Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats mark the western and eastern boundaries respectively.
- The altitude of a large portion of the plateau is more than 600 m from mean sea level.
- The peak of Anaimudi is the highest point in the plateau.
- Its height is 2,695 m and is located in Anaimalai.
- The general slope of this plateau is towards the east.
- The Great Plateau is a part of the Gondwana (very ancient one) land mass.
- Due to the old age, the rivers in this region attained their base level and developed broad and shallow valleys.
- The river Narmada divides the plateau region of India broadly into two parts.
- The region lying to the north of the Narmada is called the Central Highlands.
- The region lying to the south of Narmada is called the Deccan Plateau.
- All the major rivers (Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna, Kaveri, etc.) lying to the south of the Vindhyas flow eastwards and fall into the Bay of Bengal.
- Narmada and Tapti are the two rivers situated to the south of the Vindhyas that flow westward.
- Their movement towards the west is due to the presence of a rift valley in the region.
Central Highlands
- The Central Highlands extend between the river Narmada and the Northern Great Plains.
- The Aravallis form the west and northwestern edge of the Central Highlands.
- These hills extend from Gujarat, through Rajasthan to Delhi in the northwesterly direction for a distance of about 700 km.
- The height of these hills is about 1,500 m in the southwest while near Delhi the height is hardly 400 m.
- Gurushikhar with 1,722 m is the highest peak of this range.
- The western part of the Central Highlands is known as the Malwa Plateau.
- It lies to the southeast of Aravallis and to the north of the Vindhyachal Range.
- The rivers Chambal, Betwa, and Ken drain the Malwa Plateau before they join the river Yamuna.
- The part of the Central Highlands which extends to the east of Malwa Plateau is known as Bundelkhand and its further extension is known as Bagelkhand.
- The eastern part of the Central Highlands which lies in the north-eastern part of the Indian Plateau is known as Chhota-Nagpur Plateau.
- It covers much of Jharkhand, adjacent parts of Odisha, West Bengal, Bihar, and Chhattisgarh.
- This region is very rich in mineral resources, particularly iron ore and coal.
What's Your Reaction?