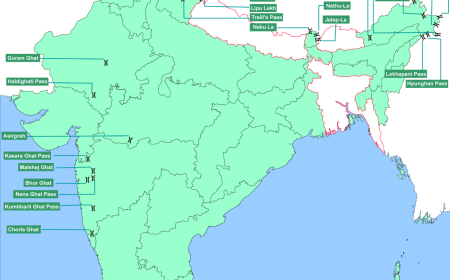
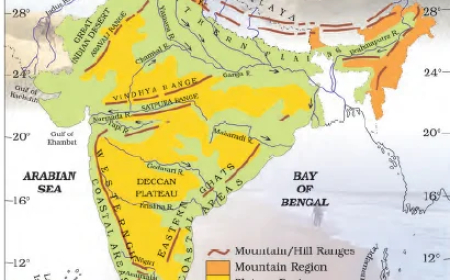
Important Passes- English
Important Passes- English
| State/UT | Passes |
|---|---|
| Jammu and Kashmir | Banihal, Bilafond La, Kongka, Mintaka, Parpik, Pir-Panjal, Qara Tag La, Sadhna, Sia La |
| Ladakh | Aghil, Chang La, Fotu La, Gyong La, Imis La, Khardung La, Lanak La, Namika La, Pensi La, Sasser La, Shingo La, Taglang La, Zoji La |
| Himachal Pradesh | Auden’s Col, Baralacha La, Chanshal, Debsa, Indrahar, Jalori, Kunzum, Lamkhaga, Rohtang, Shipki La |
| Uttarakhand | Kalindi, Lipulekh, Mana, Mangsha Dhura, Mayali, Muling La, Nama, Niti, Sin La, Traill’s |
| Sikkim | Dongkhala/Donkia, Goecha La, Jelep La, Nathu La |
| Arunachal Pradesh | Bomdila, Chankan, Dihang, Diphu, Hpungan, Kumjawng, Pangsau/Pan Saung, Sela, Yonggyap |
| Rajasthan | Goram Ghat, Haldighati |
| Maharashtra | Bhor Ghat, Thal Ghat |
| Kerala-Tamil Nadu | Palakkad gap, Shenkottai |
| Kerala | Thamarassery |
Important Mountain Passes in Jammu And Kashmir
| Mountain Passes | Strategic Importance | Elevation |
| Banihal pass | It is located across the Pir Panjal range. It connects the Kashmir valley (in Jammu and Kashmir) to the outer Himalayas. Until the construction of the Jawahar tunnel in 1956, the Banihal pass served as the road link between Jammu and Srinagar. |
2832 m |
| Bilafond La pass | Since this pass is located on the Saltoro ridge (near Siachen glacier), it is also known as the Saltoro pass. It is located near the Actual Ground Position Line (the line which divides the military posts of India and Pakistan) between India and Pakistan. It was originally a part of the ancient silk route which connected the Indian subcontinent with China. |
5450 m |
| Kongka pass | It is a low mountain pass located on the Line of Actual Control between India and China. China considers Kongka pass as the border between India and China. |
5171 m |
| Mintaka pass | It connects the Union Territory of Kashmir with China. It is located in the Karakoram mountain range and is situated near the tri-junction of India, China and Afghanistan border. |
4709 m |
| Parpik pass | It connects the Union Territory of Kashmir with China. It is located at the east of Mintaka pass on the Indo-China border. |
5467 m |
| Pir-Panjal pass | Located in the Pir Panjal range which is a group of mountains in the lesser Himalayan region. The Kashmir valley is connected to the Rajouri and Poonch districts of Jammu and Kashmir via the Pir-Panjal pass. |
3485 m |
| Qara Tag La pass | Qara Tag La is located across the Karakoram range on the Indo-China border. In the winter months, they are covered by heavy snowfall, and thus they remain closed during those months. It was a part of the ancient silk route. |
5359 m |
| Sadhna pass | Earlier, it was known as the Nastachun pass. It connects Kashmir valley to the Karnah tehsil of Jammu and Kashmir. |
3000 m |
| Sia La pass | It is situated in the Saltoro range near Siachen Glacier. In the early 1980s, it was a conflicted area between India and Pakistan. It is near the Indo-China border. |
5589 m |
Important Mountain Passes in Ladakh
| Mountain Passes | Strategic Importance | Elevation |
| Aghil pass | It lies in the Karakoram range. It separates the Ladakh region in India from the Shaksgam valley (Xinjiang province) in China. |
4805 m |
| Chang La pass | This pass connects the Ladakh region with Tibet. It lies in between the Shyok river valley and Leh district. It is one of the highest motorable roads in the world. |
5360 m |
| Fotu La pass | It is located in the Zaskar range of the Himalayas. It is one of the two mountain passes that lie between the districts of Leh and Kargil. |
4108 m |
| Gyong La pass | It is located on the Saltoro ridge southwest of Siachen Glacier. It was one of the conflicted areas between India and Pakistan. In 1989, it came under the complete control of Indian forces. |
5686 m |
| Imis La pass | It connects the Union Territory of Ladakh to Tibet in China. It remains closed during the winter months. |
5290 m |
| Khardung La pass | It is located in the Ladakh range of mountains. It serves as a gateway to Nubra and Shyok valleys. |
5359 m |
| Lanak La pass | It is located in the Aksai Chin region and thus connects India and China. While China claims Kongka pass as the border between India and China, India claims Lanak La pass as the border. |
5466 m |
| Namika La | It is located in the Zaskar range. It is one of the two mountain passes that lie between the districts of Leh and Kargil. (Fotu La is the other pass) |
3700 m |
| Pensi La pass | It is also known as the gateway to Zanskar (a tehsil in the Kargil district). It connects the Suru valley region to the Zanskar valley region. Due to heavy snowfall, it remains open only between May and October. |
4400 m |
| Sasser La pass | It connects India (Ladakh) with China. It lies in the Karakoram range in the Union Territory of Ladakh. |
5411 m |
| Shingo La pass | It is located on the border between Ladakh and Himachal Pradesh. It connects the Kargil district to the Lahaul and Spiti district of Ladakh. |
5091 m |
| Taglang La pass | Taglang La pass is one of the high-altitude mountain passes located in Ladakh. It is traversed by the Leh-Manali highway. It is the 12th-highest motorable pass. |
5328 m |
| Zoji La pass | It provides a link between Ladakh and Kashmir valley. Until the construction of the Zoji-La tunnel, this pass was closed during the winter. |
3528 m |
Important Mountain Passes in Himachal Pradesh
| Mountain Passes | Strategic Importance | Elevation |
| Auden’s Col | It is located in the Garhwal Himalayas of the Greater Himalayas range. It connects the Rudugaira valley with the Bhilangana valley. |
5490 m |
| Baralacha La pass | Baralacha La pass is situated in the Zaskar range in Himachal Pradesh. It links the Lahaul district of Himachal Pradesh to the Leh district of Ladakh. It divides the Yunam river from the Bhaga river. |
4850 m |
| Chanshal pass | This pass is situated in the highest peak of Shimla, the Chanshal peak. It links two towns in the Shimla district – Rohru and Dodra Kwar. It is also known as the Chanshal valley, and it remains open only between May and October. |
3750 m |
| Debsa pass | Debsa pass is situated between the Kullu and Spiti districts of Himachal Pradesh. It is in the Himalayan mountain range. It links the Parvati valley with the Spiti valley. |
5360 m |
| Indrahar pass | It is located in the Dhauladhar mountain range of the Himalayas. The Chamba and Kangra districts of Himachal Pradesh are separated by this pass. |
4342 m |
| Jalori pass | It lies in the northern peaks of the Himalayas and is between the districts of Kullu and Shimla. It connects the Tirthan valley with the Satluj valley. |
3134 m |
| Kunzum pass | Kunzum pass is located in the eastern Kunzum range of the Himalayas. It serves as a link between Lahaul valley and Spiti valley. It usually remains open between June and October. |
4551 m |
| Lamkhaga pass | Lamkhaga pass is located close to the Indo-Tibetan border. It connects the Kinnaur district of Himachal Pradesh with the Harshil district of Uttarakhand. |
5282 m |
| Rohtang pass | It is located on the eastern side of the Pir Panjal range of the Himalayas. It links the Kullu valley with the Lahaul and Spiti valley. |
3978 m |
| Shipki La pass | It connects India (Kinnaur district) with China (Ngari Prefecture province of Tibet) and is India’s border post between the two countries. This pass is very significant as it increases the trade between India and Tibet (China). |
3930 m |
Important Mountain Passes in Uttarakhand
| Kalindi pass | It is a high mountain pass located in the Garhwal Himalayan range of the Greater Himalayas. The water from this glaciated pass joins the Gangotri glacier located near the Indo-Tibet border. |
5950 m |
| Lipulekh pass | Lipulekh pass connects India (Uttarakhand region) with China (Tibetan region). It serves as a border between both countries. It links the Byans valley (Uttarakhand) to the Tibet Autonomous Region (China). |
5115 m |
| Mana pass | Mana pass serves as a border between India and the Tibet region of China. It is located in the Garhwal Himalayan mountain range. It is one of the highest motorable passes in India. |
5632 m |
| Mangsha Dhura pass | It is located in the Pithoragarh district of Uttarakhand. It connects Uttarakhand (India) with Tibet (China). |
5674 m |
| Mayali pass | It is located in the Uttarkashi district of Uttarakhand. It connects Bhilangana valley (in Garhwal Himalayas) with Kedarnath and Mandakini valley. |
5400 m |
| Muling La pass | It is located north of Gangotri (Uttarkashi district). It connects the Uttarakhand state of India with the Tibet region of China. |
5669 m |
| Nama pass | Nama pass is located in the Pithoragarh district of Uttarakhand. It connects India with Tibet and is one of the trade routes between India and Tibet. It also links the Kuthi valley with the Darma valley, both of which are located in the Pithoragarh district. |
5200 m |
| Niti pass | It is located on the Indo-China border and connects the Uttarakhand district with the southern region of Tibet. | 5073 m |
| Sin La pass | It is one of the high mountain passes located in the Himalayan range. For the most part of the year, this pass is covered with heavy snow. |
5495 m |
| Traill’s pass | Traill’s pass is located in between the Nanda Devi and Nanda Kot peaks of the Himalayan range. It links the Pindari glacier of the Kumaon Himalayas to the Milam glacier of the Kumaon Himalayas. |
5312 m |
Important Mountain Passes in Sikkim
| Mountain Passes | Strategic Importance | Elevation |
| Dongkhala pass / Donkia pass | It connects India with the Tibet region of China. It is located in the Himalayan mountain range. |
5534 m |
| Goecha La pass | It links Sikkim with Tibet. | 4940 m |
| Jelep La pass | It connects the Sikkim state of India with Lhasa (the administrative capital of Tibet) in China. It passes through the Chumbi valley, which is located in the eastern region of the Great Himalayan range i.e. in the southern portion of Tibet. |
4270 m |
| Nathu La pass | It connects Sikkim (India) with the Tibet Autonomous Region (China). It is one of the three trading border posts between India and China and is also one of the five border personnel meeting points between the armies of both countries. |
4310 m |
Important Mountain Passes in Arunachal Pradesh
| Mountain Passes | Strategic Importance | Elevation |
| Bomdila pass | Bomdila connects the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh with Bhutan. It is located in the western region of the Greater Himalayas. |
4331 m |
| Chankan pass | Chankan pass is located on the Indo-Myanmar border. It connects Arunachal Pradesh with Myanmar. |
2432 m |
| Dihang pass | It connects Arunachal Pradesh with the second largest city of Myanmar, Mandalay. | 4000 m |
| Diphu pass | Diphu is located at the tri-junction of India, China and Myanmar. It is on the McMohan line, which demarcates India and China. It is one of the important trade routes between India and Myanmar. |
4587 m |
| Hpungan pass | It is located on the Indo-Myanmar border. | 3072 m |
| Kumjawng pass | It connects the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh with Myanmar. | 2465 m |
| Pangsau pass / Pan Saung pass | It is located on the Patkai hills, which connect India with Myanmar. The Pangsau pass winter festival is a joint India-Myanmar event that is celebrated annually by the tribes of India and Myanmar together. |
1136 m |
| Sela pass | It is located on the border between the districts Tawang and West Kameng of Arunachal Pradesh. | 4170 m |
| Yonggyap pass | It lies on the Indo-China border and connects Arunachal Pradesh (India) with the Tibet Autonomous Region (China). | 3962 m |
Important Mountain Passes in Rajasthan
| Mountain Passes | Strategic Importance | Elevation |
| Goram Ghat | Goram Ghat connects the Udaipur city of Rajasthan with the Jalore and Sirohi districts. It is located to the south of Mount Abu and separates Gurushikar from Mount Abu. |
1200 m |
| Haldighati pass | Haldighati Pass is located in the Aravalli range (between Bagicha and Khamnor villages). It serves as a link between the Pali and Rajsamand districts of Rajasthan. It is known for the Battle of Haldighati, which took place between Maharana Pratap of Mewar and Man Singh I of Amer. |
396 m |
Important Mountain Passes in Southern India
| Mountain Passes | Strategic Importance | Elevation |
| Bhor Ghat | It is located in the northernmost region of the Western Ghats in Maharashtra. | 622 m |
| Palakkad gap / Palghat gap | It is a low mountain pass located between the Coimbatore district of Tamil Nadu and the Palakkad district of Kerala. | 140 m |
| Shenkottai pass | Shenkottai pass connects the Kollam district of Kerala to the Madurai district of Tamil Nadu. It is situated in between the Varshanadu hills and Agathiya malai. It is the second-largest gap located in the Western Ghats. |
690 m |
| Thal Ghat | Also known as the Kasara Ghat is located in the Thane district of Maharashtra. The steepest railway line in India is located on this Ghat. |
585 m |
| Thamarassery pass | Thamarassery pass is located across the Western Ghats. It connects the Kozhikode district to the Wayanad district of Kerala. It is also known as the Wayanad Churam. |
800 m |
What's Your Reaction?